The web as a graph
pagerank是谷歌用来计算网页重要性的算法,我们把网页想象成节点,超链接想象成边,这就形成了一张有向图。
当然我们只考虑静态网页,不考虑防火墙拦截、无法访问这些情况。
两种有向图:
1.强连通图Strongly connected graphs:任意节点可以到达任意节点。
2.有向无环图Directed Acyclic Graph (DAG):首先没有环,u能达到v,但v不能达到u。
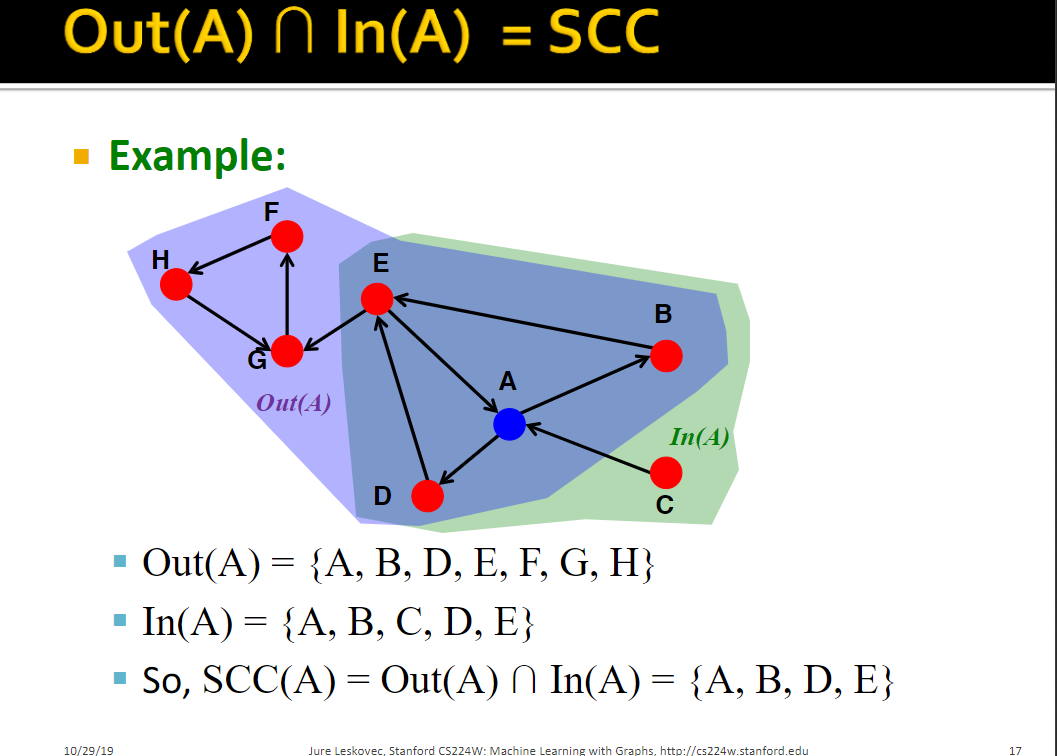
求strongly connected components (SCCs):对给定节点分别求入度和出度的BFS,然后对两个集合求交集
Bowtie structure of the web graph
Broder et al. (1999) took a large snapshot of the web and tried to understand how the SCCs in the web graph fit together as a DAG
这张图Here the starting nodes are sorted by the number of nodes that BFS visits when starting from that node
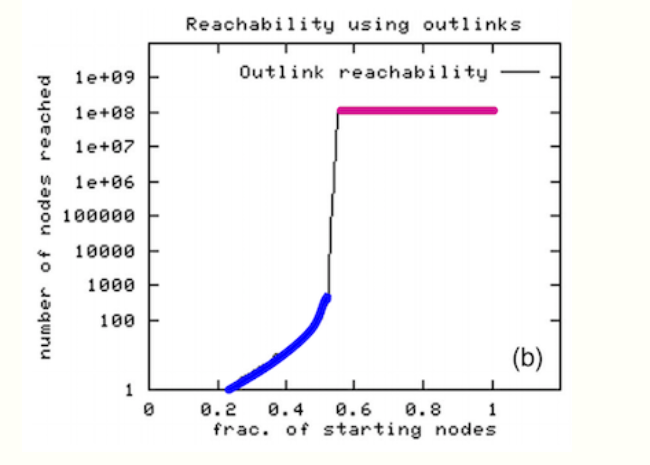
图中蓝色节点只能访问一小部分节点,紫红色节点可以访问很多节点
通过这个我们可以得出网络中的图组成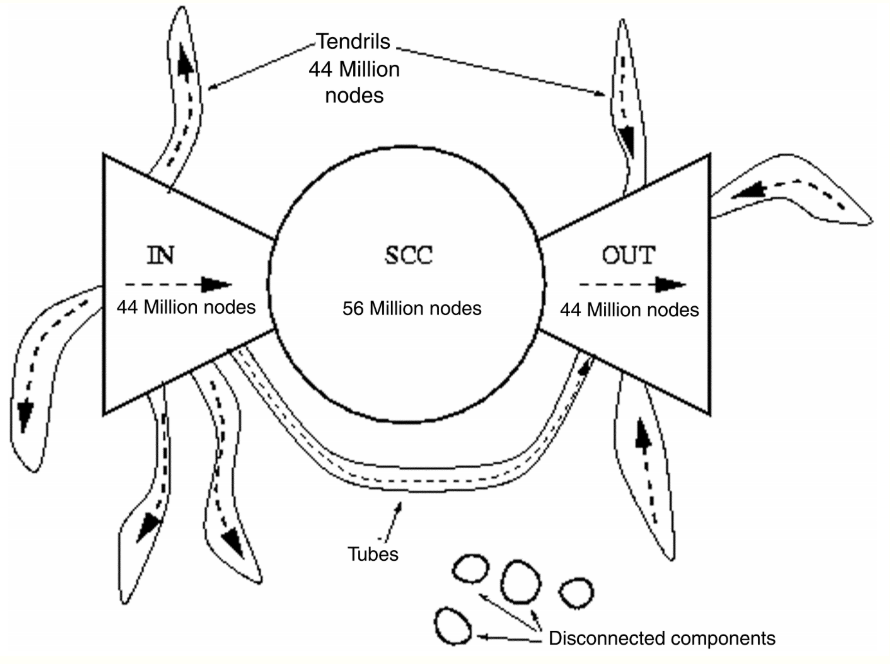
PageRank - Ranking nodes on the graph
核心想法是吧links当作votes,一个节点的重要性是由被所指向的其他节点决定的
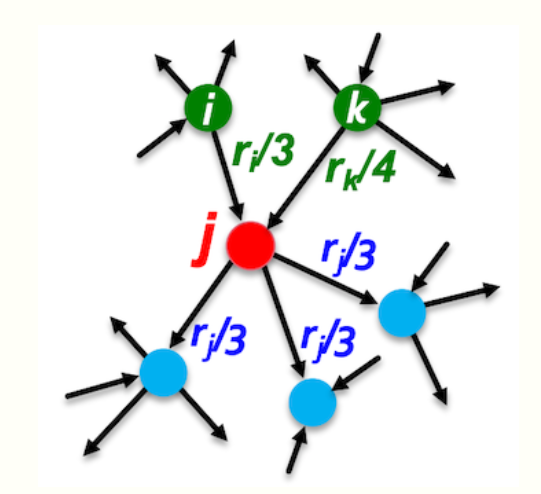
公式为
Matrix formulation
这种计算方法需要N个式子,需要很长的时间。所以我们用邻接矩阵M来代替,M的每个列的和为1,则,如下图的计算过程
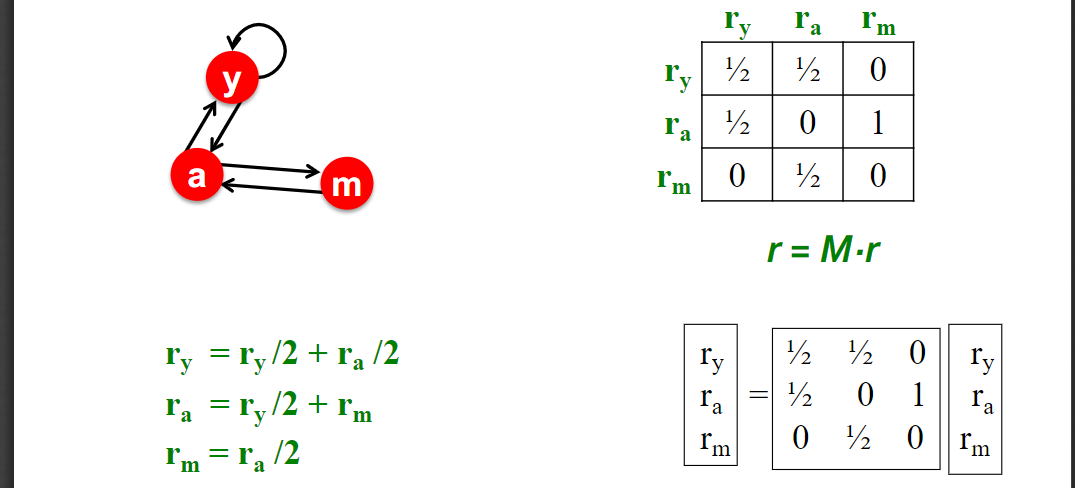
之后进行不断地迭代,直到
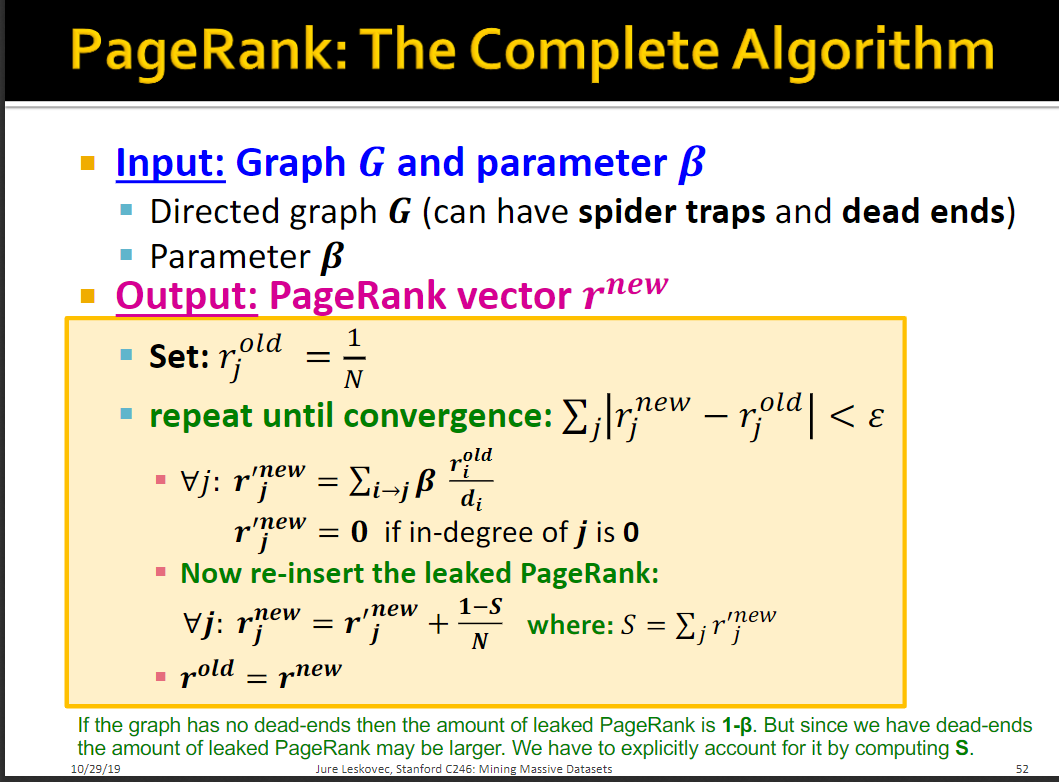
PageRank: Problems
1.dead ends:没有out-links

2.Spider traps:节点发出的边只有自环,最终会吸收所有的重要性,比如图中b会聚集所有的重要性,a会没有重要性

解决方法是random teleportation或者random jumps
当一次随机游走完成,下次网上冲浪有两种选择,有概率跟随link,跳到其它网页,跳到其他的网页节点有相同的可能性, 通常设定在0.8到0.9
综合起来就是:
下面可以定义谷歌矩阵 ,
注意这个公式假设M没有dead ends。我们可以提前处理矩阵M去除dead ends或者使用概率为1的随机random teleports
Computing PageRank: Sparse matrix formulation
但是这样对于节点太多的话,存储矩阵需要大量的空间,我们可以这样来计算: , 是一个向量,因为这样M是个稀疏矩阵,与向量乘机就没有那么大的计算量了
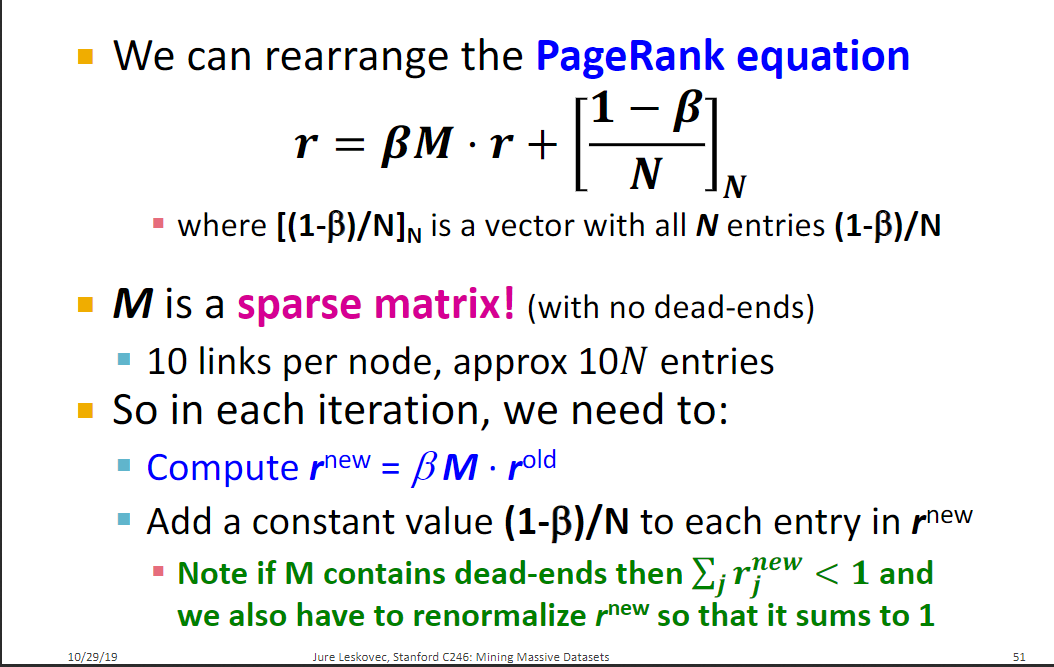
下面给出完整的算法流程